Hydrocephalus in Adults
Hydrocephalus in Adults at times suggested as “water on the frontal cortex,” is an infirmity depicted by the odd party of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) inside the psyche’s ventricles. While it is reliably associated with infant kid adolescents and teens, hydrocephalus can similarly impact adults, as occasionally as possible with colossal and huge results. This article bounces into the causes, symptoms, finding, and treatment decisions for hydrocephalus in adults, giving a hard and fast impression of this confounded condition.
What is Hydrocephalus?
Hydrocephalus happens when there is an irregularity between the creation and ingestion of cerebrospinal fluid, the undeniable fluid that combines the frontal cortex and spinal rope. CSF serves two or three fundamental limits, including padding the mind, discarding incidental effects, and remaining mindful of intracranial strain. In a sound individual, CSF is constantly made, streamed, and held. Regardless, when this concordance is disturbed, abundance liquid makes, inciting broadened burden on the mind. This can cause a degree of neurological coincidental impacts and, whenever left untreated, may accomplish serious difficulties.
Types of Hydrocephalus in Adults
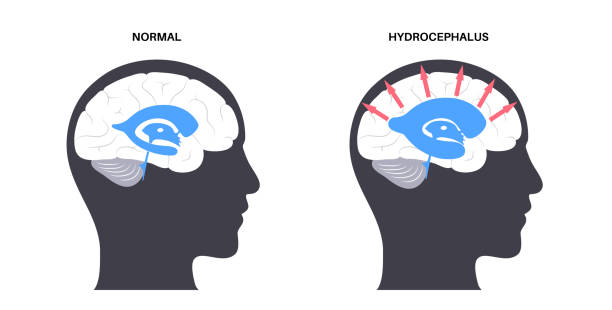
There are a few kinds of hydrocephalus that can influence grown-ups, each with particular causes and qualities:
- Normal Strain Hydrocephalus (NPH):
NPH is one of the most widely recognized types of hydrocephalus in more seasoned grown-ups. It is portrayed by the exemplary group of three of symptoms: stride aggravation, mental degradation, and urinary incontinence. In spite of the name “typical strain,” the condition includes discontinuous expansions in intracranial tension. NPH is in many cases idiopathic, meaning the specific reason is obscure, however it can likewise result from conditions, for example, subarachnoid discharge, meningitis, or horrible cerebrum injury. - Obstructive Hydrocephalus:
This type happens when there is an actual blockage in the progression of CSF, frequently because of growths, pimples, or inborn irregularities. The blockage keeps CSF from circling appropriately, prompting liquid development and expanded intracranial tension. - Communicating Hydrocephalus:
Here, the progression of CSF isn’t impeded, yet the liquid isn’t ingested as expected into the circulation system. This can result from aggravation, contamination, or draining in the mind. - Secondary Hydrocephalus:
This type creates because of another hidden condition, like a cerebrum injury, stroke, or disease. The harm brought about by these circumstances upsets the typical stream or retention of CSF.
Symptoms of Hydrocephalus in Adults
The symptoms of hydrocephalus in adults can move dependent upon the sort and earnestness of the condition. In any case, a few normal symptoms include:
- Cognitive Changes: Adults with hydrocephalus could experience mental degradation, inconvenience cantering, and hindered abilities to think. These psychological changes can be inconspicuous immediately anyway may progress long term, influencing everyday working and individual fulfilment.
- Gait Disturbances: One of the brand name symptoms of normal strain hydrocephalus (NPH) is inconvenience walking. Patients could show a modifying step, balance issues, and an inclination to fall. This aftereffect is regularly mistaken for a sign of developing or other neurological conditions.
- Urinary Incontinence: Hydrocephalus can impact the frontal cortex’s control over bladder ability, provoking urinary criticalness, repeat, or incontinence. This secondary effect is particularly typical in NPH and can be disturbing for patients.
- Headaches: Extended intracranial strain due to hydrocephalus can cause innovative headaches, regularly joined by nausea and disgorging. These headaches could wreck close to the start of the day or after genuine work.
- Vision Problems: Hydrocephalus can apply pressure on the optic nerve, provoking clouded vision, twofold vision, or inconvenience focusing. In serious cases, it could achieve vision mishap.
- Fatigue and Lethargy: Adults with hydrocephalus regularly report feeling excessively depleted or torpid, even after palatable rest. This shortcoming can disturb ordinary activities and by and large thriving.
- Mood Changes: Hydrocephalus can in like manner impact perspective, provoking irritability, awfulness, or strain. These significant changes may be associated with the psychological and genuine challenges related with the condition.
Causes of Hydrocephalus in Adults
Hydrocephalus in adults can arise from a variety of causes, including:
- Traumatic Psyche Injury (TBI): Head wounds, similar to those upheld in car accidents or falls, can provoke depleting or expanding in the frontal cortex, disturbing the movement of CSF and causing hydrocephalus.
- Infections: Pollutions of the central tangible framework, similar to meningitis or encephalitis, can cause irritation and scarring that blocks CSF stream.
- Brain Tumors: Developments in the frontal cortex or spinal rope can impede the ventricles or the pathways through which CSF streams, provoking hydrocephalus.
- Subarachnoid Haemorrhage: Depleting in the space between the brain and the enveloping film (subarachnoid space) can result from a burst aneurysm or other vascular inconsistencies, causing hydrocephalus.
- Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus (NPH): NPH is a large part of the time idiopathic, importance its exact explanation is dark. Regardless, it is more typical in more prepared adults and may be connected with conditions like Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s affliction, or past frontal cortex wounds.
- Congenital Hydrocephalus: While hydrocephalus is ordinarily dissected in beginning, a couple of individuals may not experience secondary effects until adulthood. This deferred start can happen due to simple irregularities in CSF stream that weaken long term.
- Other Clinical Conditions: Certain illnesses, similar to stroke, different sclerosis, or intricacies from mind an operation, can moreover add to the improvement of hydrocephalus in adults.
Diagnosis of Hydrocephalus in Adults
Diagnosing hydrocephalus in adults requires a thorough evaluation by a healthcare professional, regularly including a mix of clinical assessment, imaging survey, and decisive tests. Coming up next are typical illustrative techniques:
- Medical History and Physical Examination: A detailed medical history and physical examination are central for recognizing secondary effects and potential bet factors for hydrocephalus. The clinical benefits provider could review mental capacity, step, and bladder control.
- Imaging Studies: Imaging methodology, for instance, computed tomography (CT) channels and magnetic resonation imaging (MRI) are fundamental for imagining the frontal cortex’s ventricles and recognizing any abnormalities in CSF stream. These imaging studies can help with isolating between different sorts of hydrocephalus and block various conditions.
- Lumbar Puncture (Spinal Tap): A lumbar Puncture incorporates killing a restricted amount of CSF from the lower back to check its strain and inspect its association. This test can help with diagnosing regular pressure hydrocephalus (NPH) and overview the sufficiency of treatment.
- Intracranial Pressure Monitoring: In some cases, industrious checking of intracranial pressure may be vital to assert the examination and guide treatment decisions.
- Neuropsychological Testing: Neuropsychological tests may be directed to evaluate mental capacity, memory, and decisive reasoning skills, giving critical pieces of information into the impact of hydrocephalus on the brain.
Treatment Options for Hydrocephalus in Adults
The treatment of hydrocephalus in grown-ups relies upon the basic reason, the seriousness of symptoms, and the patient’s general health. The basic objective of treatment is to diminish intracranial strain and re-establish ordinary CSF stream. Coming up next are typical treatment decisions:
- Surgical Intervention: Operation is much of the time the best treatment for hydrocephalus. The most broadly perceived a medical procedure is what is going on of a shunt, a versatile chamber that diverts excess CSF from the frontal cortex to another piece of the body, similar to the waist, where it might be held. Shunts are regularly equipped with a valve that controls the movement of CSF to thwart over-squander.
- Endoscopic Third Ventriculostomy (ETV): on occasion, an ETV may be continued as a decision to shunt circumstance. This irrelevantly prominent strategy remembers making somewhat opening for the floor of the third ventricle to allow CSF to evade the block and stream energetically.
- Medications: While solutions can’t fix hydrocephalus, they may be used to administer aftereffects or reduce CSF creation in unambiguous cases. Diuretics, for instance, acetazolamide, are sometimes prescribed to lessen CSF creation momentarily.
- Rehabilitation and Solid Care: Adults with hydrocephalus could benefit from dynamic recovery, word related treatment, and mental rebuilding to address walk disrupting impacts, further foster convey ability, and redesign mental ability. Consistent thought, including coordinating and support social events, can moreover help patients and their families with adjusting to the significant and mental troubles of living with hydrocephalus.
- Regular Checking and Follow-Up: Patients with hydrocephalus require nonstop seeing to study the suitability of treatment and perceive any disarrays, for instance, shunt error or tainting. Standard resulting gatherings with a sensory system trained professional or neurosurgeon are central for long stretch the chiefs.

Living with Hydrocephalus
Living with hydrocephalus can be trying, yet with proper treatment and sponsorship, various adults with the condition can have fulfilling existences. Patients should adhere to their therapy plan, go to customary resulting courses of action, and search for help from medical consideration specialists, family, and care gatherings. Early investigation and mediation are basic to restricting the impact of hydrocephalus on mental and genuine capacity.
[sp_easyaccordion id=”4697″]
Conclusion
Hydrocephalus in grown-ups is a complex and frequently misconstrued condition that requires convenient finding and proper treatment. By sorting out the symptoms, causes, and therapy decisions, patients and clinical benefits providers can collaborate to manage the condition effectively and work on private fulfilment. Advances in clinical development and ceaseless assessment offer expect further developed results and new treatment decisions later on. If you or a companion or relative is experiencing symptoms of hydrocephalus, it is fundamental for search for medical thought expediently to ensure the best outcome.

Dr. Hamza is a medical content reviewer with over 12+ years of experience in healthcare research and patient education. He specializes in evidence-based health information, medications, and chronic conditions. His reviews are grounded in trusted medical sources and current clinical guidelines to ensure accuracy, transparency, and reliability. Content reviewed by Dr. Hamza is intended for educational purposes and is not a substitute for professional medical advice.